Last Updated on: January 19, 2024
Edited By: Alfred
- It gives the body a structure and shape and provides the necessary support to stand. It also allows the body to move around. Without the spine, humans would have been vegetables, and wriggled around, without a proper support to stand.
- It protects the spinal cord which is a column of nerves that connects the brain with rest of the body and enables humans to control their movements.
- It is also important for normal functioning of the organs as it carries messages from the brain to rest of the body parts.
- The natural curve of the spine between the brain and the pelvis is designed to functions as a shock absorber during movements.
- It distributes body weight evenly.
In the initial phases (hyper-lordotic), the patients may be mildly affected, where the issue may not cause any pain or symptoms. But if the spine is subjected to abnormal stress, it can lead to loss of lordosis. Lordosis Causes:-
- Congenital anomaly – During fetal development, there may be irregular lordotic development due to which the front and back discs do not have the same thickness. Due to this, the individual vertebra tips slightly and increases the normal curvature of the spine.It is one of the major lordosis causes.
- Tight low back muscle- In this case it may cause an imbalance on the posture and exert excess pressure on the spine.
- Weak hamstrings and tight hip flexors
- Pregnancy- During pregnancy, the anterior weight of the women can increase, due to which the pressure on the spine is more than what it can take. This leads to loss of lordosis.
- Flat back– It can occur after spinal fusion surgery and is called as flat-back.
- Deficiency of vitamin D– The deficiency of this vitamin causes rickets which can also lead to this condition.
- Pot belly/Paunch– Men with a heavy stomach have a similar effect on the spine as pregnant women. Due to this the spine develops an abnormal curve causing loss of lordosis.
- Sitting posture- Wrong sitting posture, continuously for hours, which are characterized by stooped shoulders, can also cause this condition.
- Discitis – inflammation of the intervertebral disc space.
- Osteoporosis- The decrease in the bone density can cause vertebrae to loose strength and have an abnormal curvature which leads to loss of lordosis.
- Spondylolisthesis– this is a condition in which one vertebra in the lumbar spine slips forward in relation to an adjacent one.
- Hereditary– Usually loss of lordosis has a family history, where most of the members suffer from this condition after a certain age.
- Obesity- The spine is deigned to support a certain amount of weight. When the weight rises above the spines carrying capability, it tends to develop an abnormal curve which leads to loss of lordosis.
Lordosis Symptoms:- The??lordosis symptoms vary depending on the part of the spine that is affected. The generalized lordosis symptoms consists of ‘
- Pain in the localized area especially during movements.
- Abnormal standing posture especially while standing.
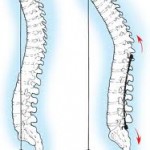
- Forward spinal curvature of the lower back.
- Numbness in the affected area such as the nape of the neck, or small of back
- Muscle spasms.
- Tingling sensation in the affected area.
- Weakness and bowel/bladder changes.
The best way to diagnose this disorder is by taking PA (posterior/anterior or back to front) and lateral (side) X- rays. The X-rays show the degree of curvature. Lordosis Treatment- Depending on the level of curvatures, the doctor chooses between surgical and non surgical lordosis treatments.
- Non surgical Lordosis Treatment – This is when the curvature is not to steep and is not affecting the movements of the body.
- Pain killers and anti-inflammatory medications help to ease the pain and ensure that there is no inflammation.
- Physiotherapy- this helps to rebuild the strength, flexibility and helps to perform daily tasks better.
- The patient may be put on braces around the affected area, especially if the patient is an adolescent who is in the growing phase.
- If the cause of loss of lordosis is obesity, then the patient is advised to loose weight.
- Surgical Lordosis Treatment – Surgery is considered if the spinal cord is getting affected which is leading to tingling, loss of sensation or muscle spasm. Based on the condition, front or back surgery is performed.
Post non-surgical Lordosis Treatments doctors recommend back exercises and a healthy diet that is rich in calcium. This can help correct the posture, strengthens the abdominal muscles and increases the spine flexibility. Post-operative care involves regular follow-ups with the doctor. Usually the doctor recommends home customized programs.

Comments are closed.